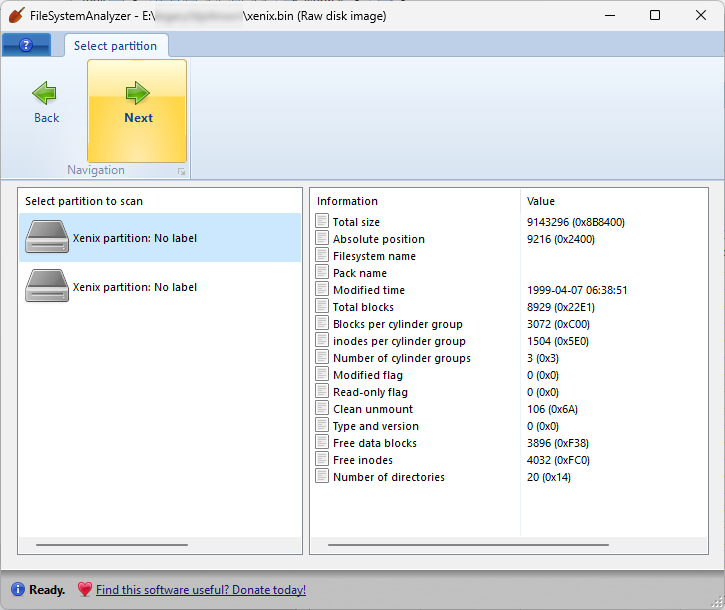
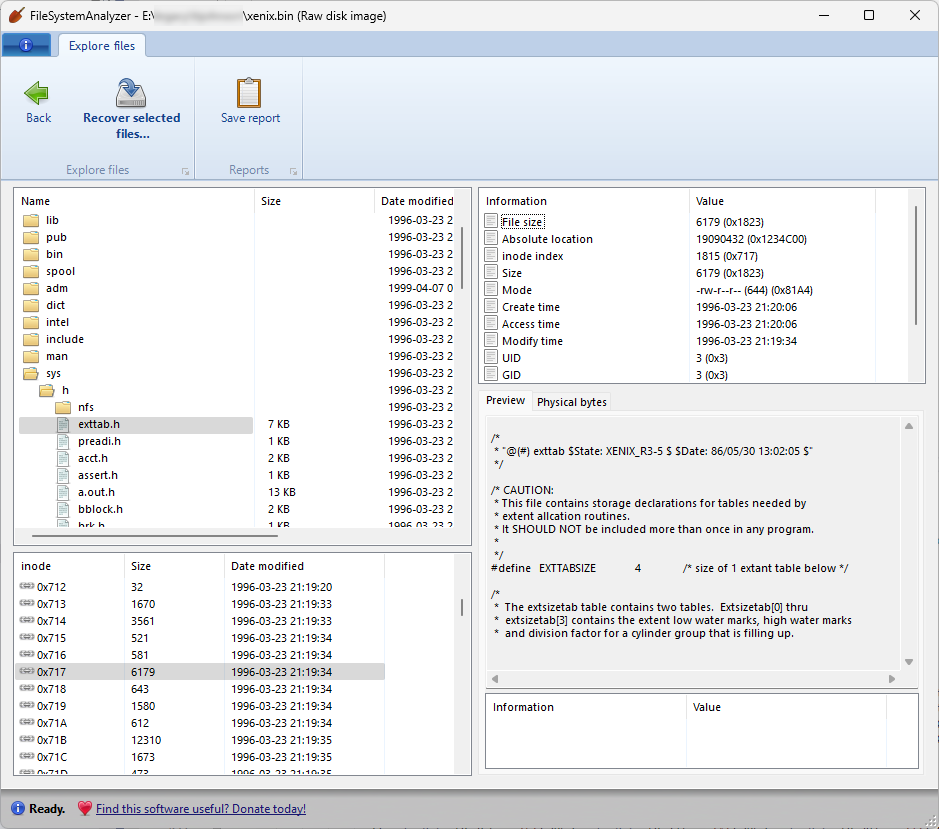
I’ve finished some major updates to DiskDigger, as well as its companion tool FileSystemAnalyzer, to support a few more filesystems, some more obscure than others!
ReFS support
One of these filesystems represents a serious and substantial update: DiskDigger now has expanded support for ReFS, the Resilient File System introduced in recent versions of Windows Server and Windows Enterprise editions. ReFS remains totally proprietary and undocumented, so it required quite a bit of reverse-engineering to nail down the structures that it uses. I’m happy to report that DiskDigger now supports versions of ReFS starting from 3.0 (introduced in Windows Server 2016) through the very latest version 3.12 (in the latest insider build of Windows 11 Enterprise).
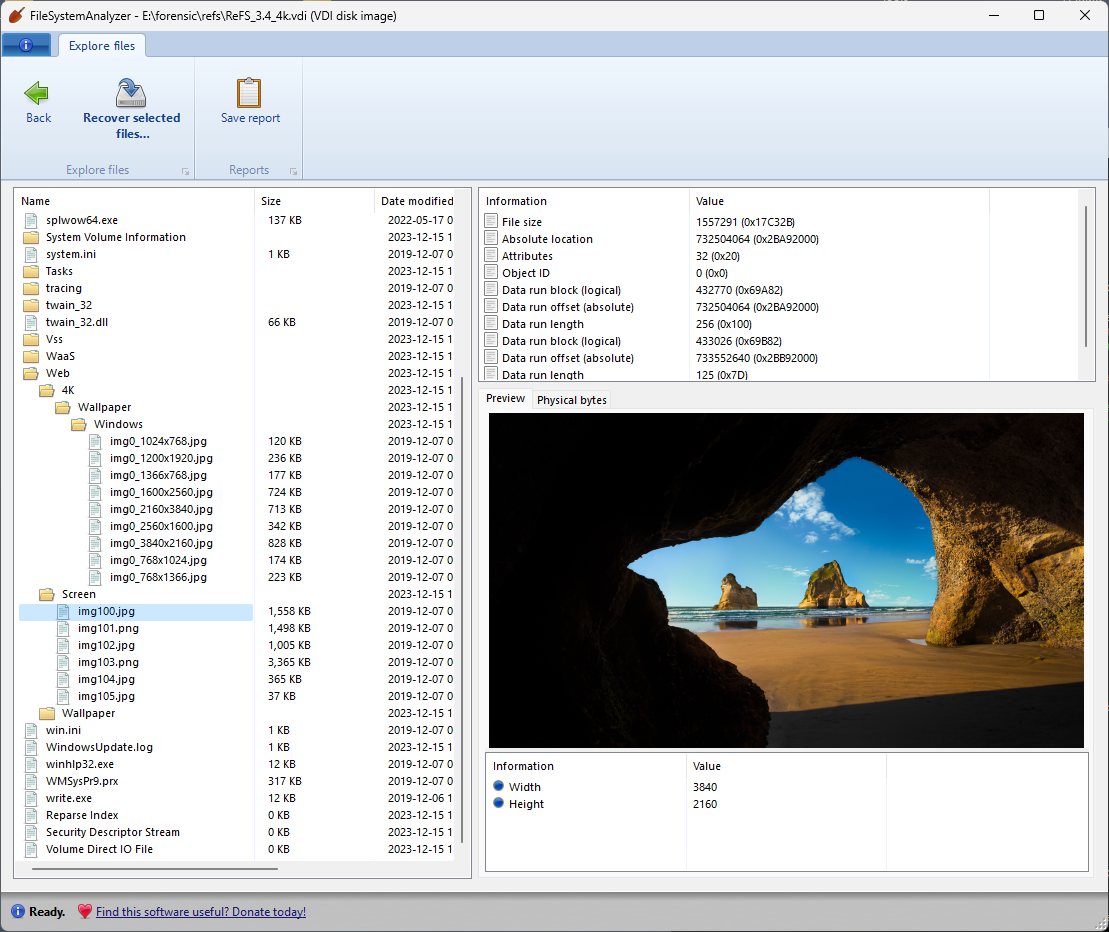
To be clear, DiskDigger had already been able to recover data from ReFS partitions by performing a heuristic (carving) search, which is independent of the actual filesystem on the disk. But now that it understands the data structures of ReFS, it can employ additional specific techniques to recover files more accurately from such partitions.
And on a lighter, more whimsical note, DiskDigger and FileSystemAnalyzer now support two other filesystem types that you’ll likely never encounter in everyday life:
RedSea filesystem
The RedSea filesystem was created by the late Terry Davis as part of his TempleOS operating system. If you’re not familiar with TempleOS, it’s an interesting rabbit hole to delve into. Literally an entire operating system built by a single person over the course of many years, TempleOS is intended to be “god’s third temple” in the form of an operating system, due to the guiding principles behind the operating system that Davis believed he was receiving from god. These principles are largely based around simplicity and purity, which is something that even the most hardened atheist like myself can appreciate. There is an expansive volume of videos in which Davis provides tutorials and explains the various features and design choices of TempleOS.
Terry was a troubled soul: he was living with uncontrolled schizophrenia which led to his eventual demise, and his videos occasionally contain some bizarre and horribly racist commentary, all of which make him more pitiable than admirable as a person. However, he was an undeniable savant at building an operating system, and I will defend the idea that we can learn something from his kernel, his compiler, and his insistence on simplicity. As a tribute to his work, I’m including support for the RedSea filesystem in DiskDigger and FileSystemAnalyzer.
The RedSea filesystem is, in many ways, the simplest filesystem possible:
- All files are contiguous! There’s no concept of fragmentation.
- There are no B-trees, no journaling, no symbolic links, no encryption, etc.
- There’s no concept of clusters; block sizes are the same as sector sizes, i.e. 512 bytes.
- Directory blocks are just a sequential list of directory entries.
- For determining where to write new files, there is simply an allocation bitmap, where each bit represents whether the corresponding block is allocated.
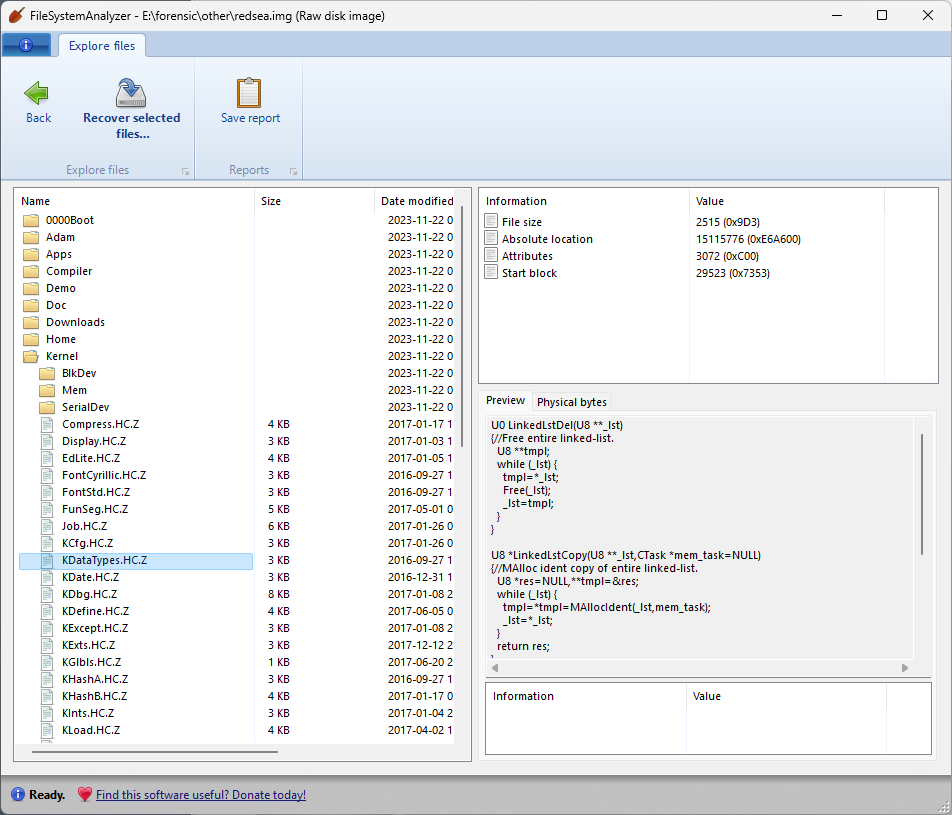
One other interesting feature of the RedSea filesystem is that it performs a sort of semi-automatic compression of files, using a form of LZW compression. If you give a file a name that ends with a “.Z” extension, it will be compressed when it’s written to the disk, and then uncompressed the next time it’s read from the disk (transparently to the user). This compression is also supported in DiskDigger, i.e. files recovered from a RedSea partition will be automatically uncompressed.
Commodore 64 disk images
As another fun diversion, I also added support for Commodore 64 disk images (D64 files)! The file system on these disks is thoroughly documented, and is also very simple: files are represented as a linked list of blocks (a primitive “block chain”, as it were). If you have these disk images lying around, you can now peruse their contents!
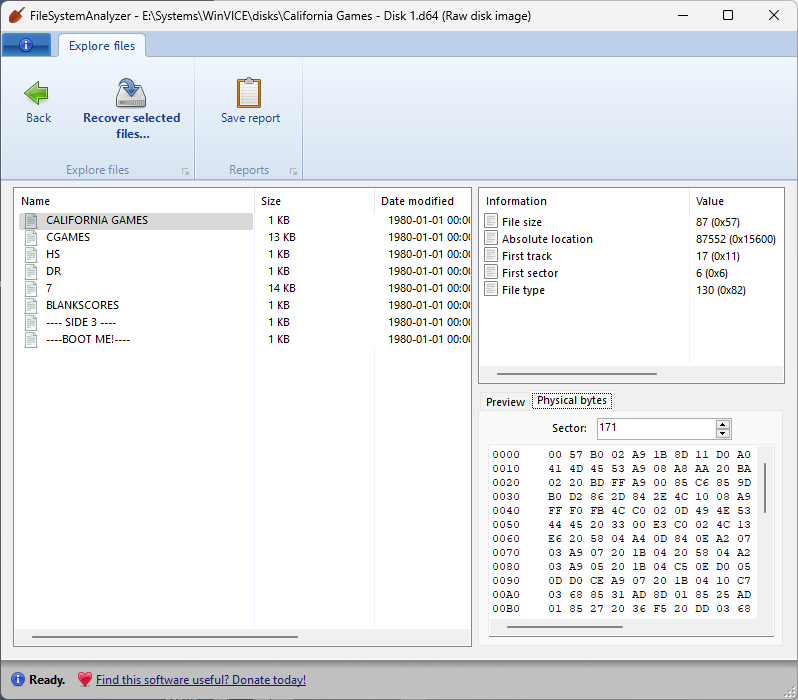
As with all filesystems supported by FileSystemAnalyzer and DiskDigger, these additions are read-only, since these are intended to be tools for forensic analysis, and not intended for two-way interoperability.